okikiko.com – While the cause of osteoarthritis is unknown, symptoms can include a deterioration in the joints and loss of elasticity. The earliest symptoms may be mild and are not indicative of a more serious condition. Osteoarthritis can affect any joint in the body, including the knees, hips, spine, hands, and big toes. Knee osteoarthritis is most common and usually affects both knees. Hip osteoarthritis, which affects the ball-and-socket joint, is equally common in men and women.
Physically demanding occupations and repetitive activities increase the risk of osteoarthritis

A major injury can lead to osteoarthritis in a particular joint later in life. Physically demanding jobs and repetitive activities increase the risk of osteoarthritis. In rare cases, certain childhood abnormalities may lead to earlier development of the disease. Genetics may also affect your risk of osteoarthritis. Some types of osteoarthritis are caused by mutations of one gene, affecting a protein called collagen.
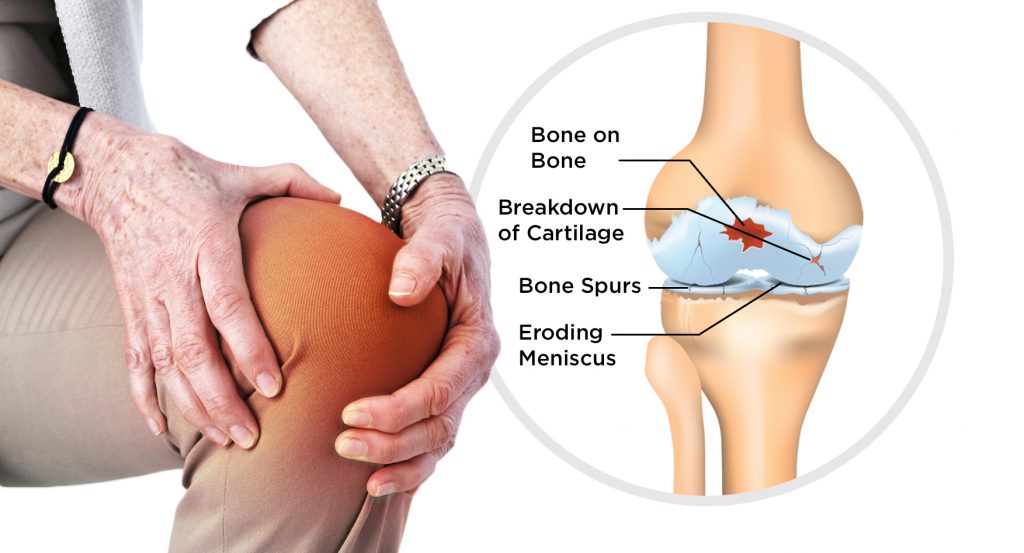
People with OA usually experience stiffness and pain in the joints, which worsens with age. The edge of the joints may be swollen, and the fingers may be red, tender, or tender. Stage four of osteoarthritis results in severe pain, a loss of joint flexibility, and bone spurs in the joint. Prescription pain relievers are the main treatment for this disease. Surgery may be necessary if the symptoms are severe enough to interfere with the quality of life.
X-rays are not always helpful in determining the cause of the osteoarthritis
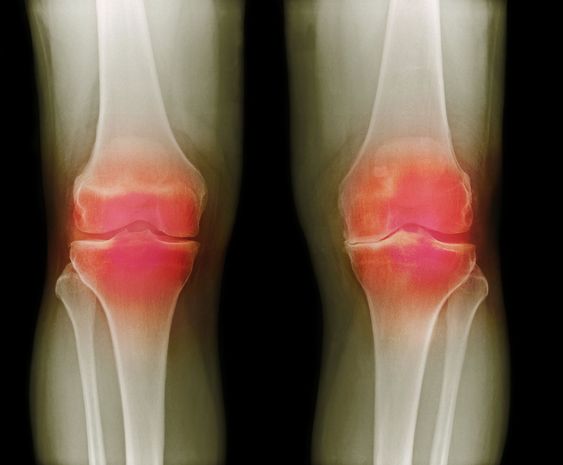
Radiographs are an important diagnostic tool in determining the cause of osteoarthritis. This is important because the appearance of osteophytes in the joint is a definite sign of the disease. While osteoarthritis can be triggered by a variety of other conditions, it is not always accompanied by joint pain. X-rays are not always helpful in determining the cause of osteoarthritis, but an MRI can help rule out other possible conditions that are affecting the joint.
Some symptoms of osteoarthritis may appear in middle age. In some cases, osteophytes are the cause of the disease. These small irregular bone growths cause swelling and pain and can impair movement. Family members may also carry the same genes as those with OA. Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, medications, and surgery can improve symptoms. However, symptoms of this disease often worsen at night and continue during the day.
The right athletic gear can reduce the impact on joints

If the condition is diagnosed early, it may be possible to alter your sports or exercise routine. While genetics can’t be changed, taking care of your body can greatly reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Proper athletic gear can reduce the impact on joints. Various shoes are designed to provide support, stability, and safety to the joints. For individuals who find exercise and sports difficult, aqua jogging may be an option.
Genetic factors and repetitive joint movements are known to increase the risk of developing OA. MRI scans and X-rays can help confirm the diagnosis of OA and other diseases. Joint fluid analysis and blood tests can rule out infections and gout. MRIs are useful in determining the type of arthritis. These tests can help your physician find the root of your pain and decide whether or not to recommend further treatment.
For severe cases, stronger anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed
In some cases, NSAIDs can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Ibuprofen (Tylenol) and diclofenac are common over-the-counter medications. For severe cases, stronger anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. You can apply topical medications to relieve pain, while other methods, such as acupuncture, are also effective. You can also consider weight loss and exercise as non-pharmacologic treatments for osteoarthritis.
Occupational and physical therapy are also common treatments for OA. Occupational therapists teach patients exercises to reduce pain and strengthen joints, and can help with pain management. Joint injections are effective for mild to moderate symptoms, but use caution. They may interact with other medications and have side effects. A stronger pain reliever may be prescribed. You should avoid overuse of acetaminophen and ibuprofen because they may damage joints.